M-Bus – Hardware components
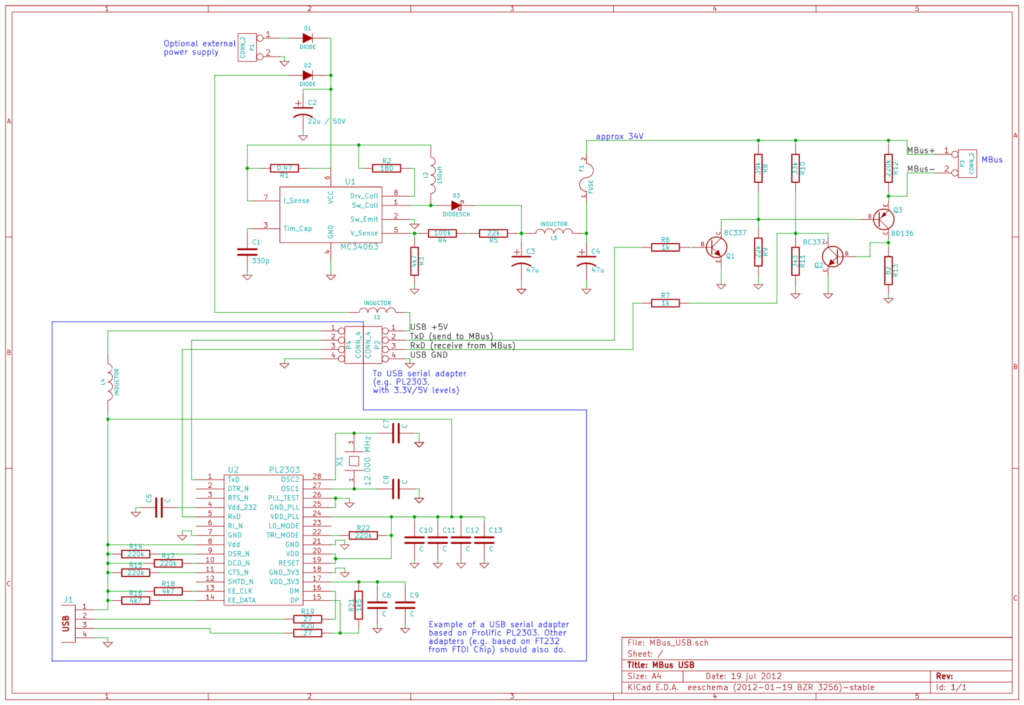
M-Bus to USB schematic example
The convertor is very simple – there are three main parts:
– MBus level converter
– power Voltage converter
– USB serial converter
Voltage converter – “catalogue” use of MC34063 in step-up configuration set for about 34V output voltage and few tens of mA. You can use any other IC/setup which would do the job. Note that if you use other voltage output than 34V (note the MBus limits) you need to adjust the voltage divider (see below) or use 12V Zener diode instead of R9.
MBus level converter – it is based on the original design from Uni Paderborn (http://www.m-bus.com/files/minimaster.tif or http://www.m-bus.de/pw1.shtml). It was just “inverted” to use common ground and low voltage IO signals. Also the 12V output voltage drop is done by simple divider (R9/R8) which is OK here (stable voltage, current is amplified).
Basically no part of the convertor is critical – except of the 12V diff (see above) and current sensing R12.
The USB serial convertor is not covered here in much detail as it does not make sense to build one. Get a USB serial cable – ideal one is an old phone data cable as these are without the RS232 level convertor (i.e. exactly what we want).
One sidenote explanation. Typical USB RS232 cable contains two main chips: USB to TTL/CMOS serial converter (this is the “smart” one – e.g. variants of FTDI Chip FT232 or Prolific PL2303) and TTL/CMOS to RS232 voltage converter (variants of MAX232). We need just the first part as we have our own voltage converter – here CMOS/TTL to MBus instead.
Or you can buy this as a module.
The bottom line is – get either a cable which does not have the RS232 converter or a cable which can be easily opened/dissected and the converter bypassed.
Finally the disclaimer – this is for educational purposes, there is no warranty of any sort.
From technical perspective this works only for few slaves as it is only a simple converter and the power is very limited as well. Tested with the bus of few tens of meters with speed up to 9600Bd with no problems.
Contributed by Tomas Menzl.
Source: https://github.com/rscada/libmbus/tree/master/hardware
Ps. you only need this small piece of the schematic for interface uses only:
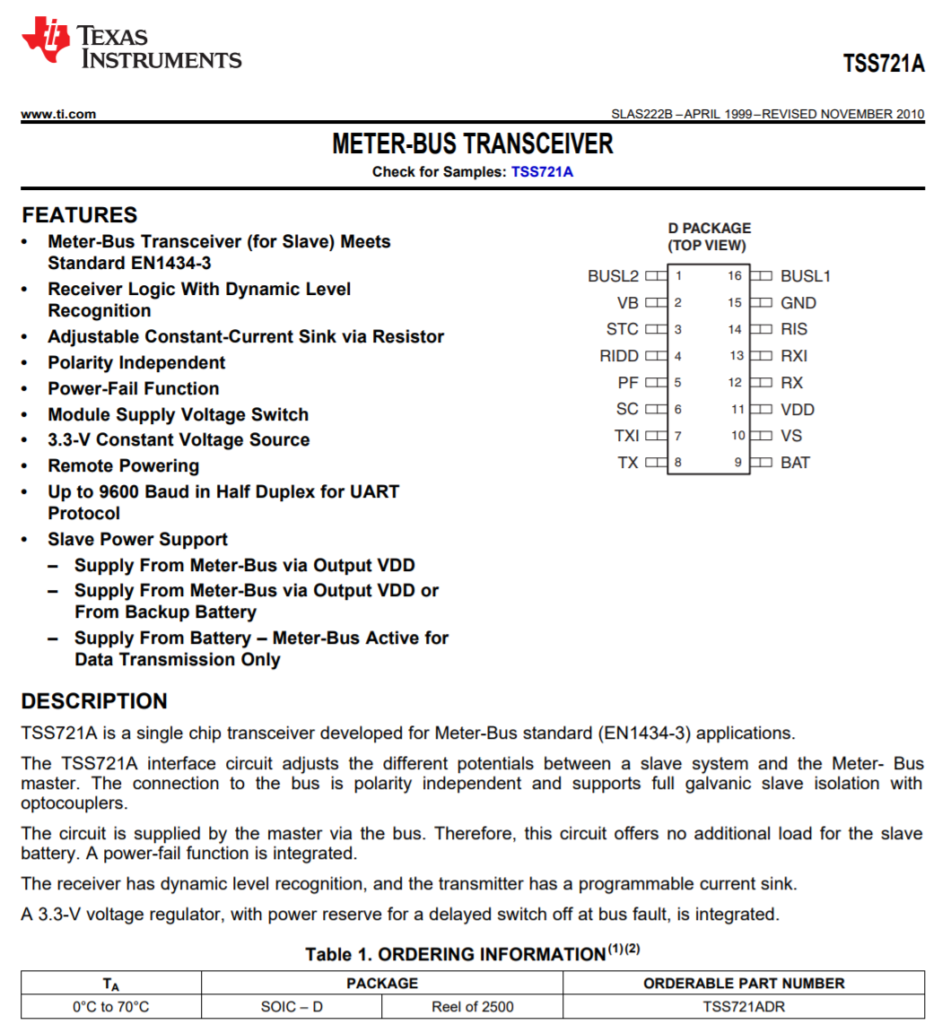
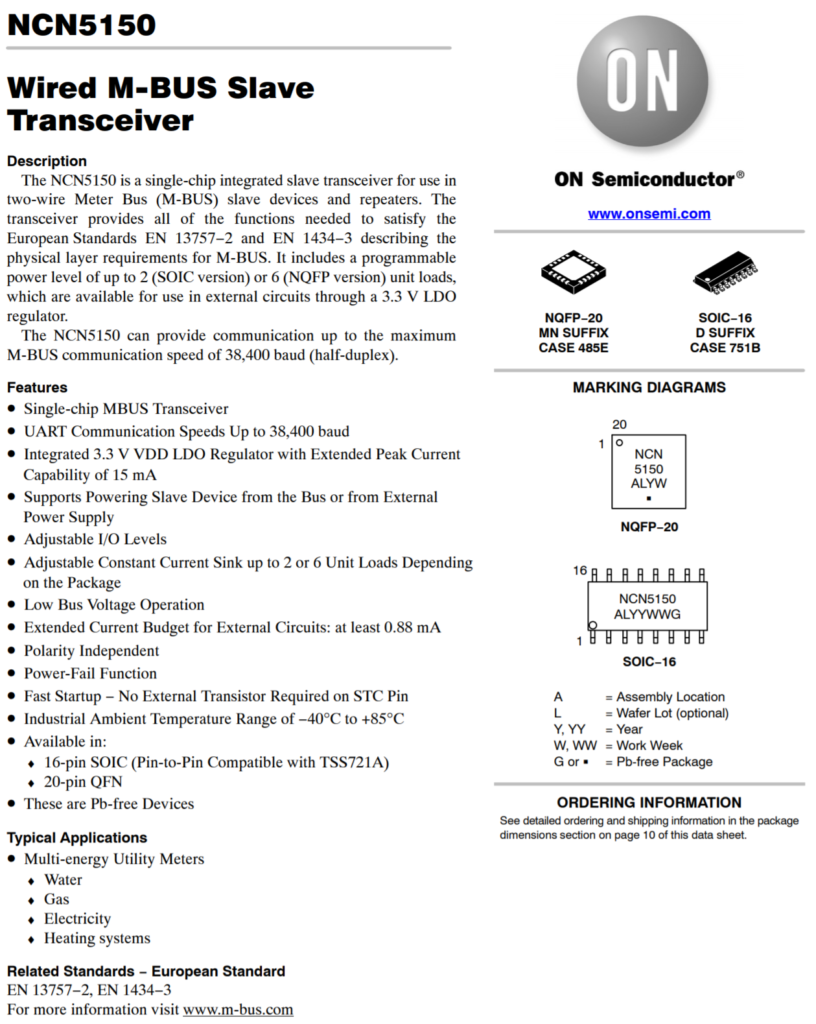
Other IC’s that could be used as M-bus trancievers
To be compatible with any common M-Bus master / M-Bus Software, you have to implement the protocol stack according to EN13757.
So yes, in general its totally possible to implement this on a Arduino or RPI.