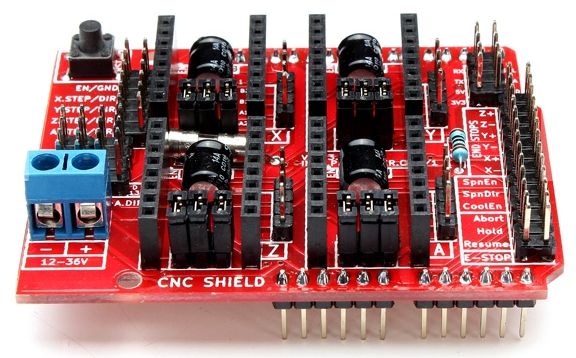
Mechanica Firmware – GRBL (Arduino CNC Shield)
Hardware
GRBL pinout op Arduino:
Informatie (ENG)
Grbl is a no-compromise, high performance, low cost alternative to parallel-port-based motion control for CNC milling. This version of Grbl runs on an Arduino with a 328p processor (Uno, Duemilanove, Nano, Micro, etc).
The controller is written in highly optimized C utilizing every clever feature of the AVR-chips to achieve precise timing and asynchronous operation. It is able to maintain up to 30kHz of stable, jitter free control pulses.
It accepts standards-compliant g-code and has been tested with the output of several CAM tools with no problems. Arcs, circles and helical motion are fully supported, as well as, all other primary g-code commands. Macro functions, variables, and most canned cycles are not supported, but we think GUIs can do a much better job at translating them into straight g-code anyhow.
Grbl includes full acceleration management with look ahead. That means the controller will look up to 16 motions into the future and plan its velocities ahead to deliver smooth acceleration and jerk-free cornering.
- Licensing: Grbl is free software, released under the GPLv3 license.
- For more information and help, check out our Wiki pages! If you find that the information is out-dated, please to help us keep it updated by editing it or notifying our community! Thanks!
- Lead Developer: Sungeun “Sonny” Jeon, Ph.D. (USA) aka @chamnit
- Built on the wonderful Grbl v0.6 (2011) firmware written by Simen Svale Skogsrud (Norway).
Update Summary for v1.1
- IMPORTANT: Your EEPROM will be wiped and restored with new settings. This is due to the addition of two new spindle speed ‘$’ settings.
- Real-time Overrides : Alters the machine running state immediately with feed, rapid, spindle speed, spindle stop, and coolant toggle controls. This awesome new feature is common only on industrial machines, often used to optimize speeds and feeds while a job is running. Most hobby CNC’s try to mimic this behavior, but usually have large amounts of lag. Grbl executes overrides in realtime and within tens of milliseconds.
- Jogging Mode : The new jogging commands are independent of the g-code parser, so that the parser state doesn’t get altered and cause a potential crash if not restored properly. Documentation is included on how this works and how it can be used to control your machine via a joystick or rotary dial with a low-latency, satisfying response.
- Laser Mode : The new “laser” mode will cause Grbl to move continuously through consecutive G1, G2, and G3 commands with spindle speed changes. When “laser” mode is disabled, Grbl will instead come to a stop to ensure a spindle comes up to speed properly. Spindle speed overrides also work with laser mode so you can tweak the laser power, if you need to during the job. Switch between “laser” mode and “normal” mode via a
$setting.- Dynamic Laser Power Scaling with Speed : If your machine has low accelerations, Grbl will automagically scale the laser power based on how fast Grbl is traveling, so you won’t have burnt corners when your CNC has to make a turn! Enabled by the
M4spindle CCW command when laser mode is enabled!
- Dynamic Laser Power Scaling with Speed : If your machine has low accelerations, Grbl will automagically scale the laser power based on how fast Grbl is traveling, so you won’t have burnt corners when your CNC has to make a turn! Enabled by the
- Sleep Mode : Grbl may now be put to “sleep” via a
$SLPcommand. This will disable everything, including the stepper drivers. Nice to have when you are leaving your machine unattended and want to power down everything automatically. Only a reset exits the sleep state. - Significant Interface Improvements: Tweaked to increase overall performance, include lots more real-time data, and to simplify maintaining and writing GUIs. Based on direct feedback from multiple GUI developers and bench performance testing. NOTE: GUIs need to specifically update their code to be compatible with v1.1 and later.
- New Status Reports: To account for the additional override data, status reports have been tweaked to cram more data into it, while still being smaller than before. Documentation is included, outlining how it has been changed.
- Improved Error/Alarm Feedback : All Grbl error and alarm messages have been changed to providing a code. Each code is associated with a specific problem, so users will know exactly what is wrong without having to guess. Documentation and an easy to parse CSV is included in the repo.
- Extended-ASCII realtime commands : All overrides and future real-time commands are defined in the extended-ASCII character space. Unfortunately not easily type-able on a keyboard, but helps prevent accidental commands from a g-code file having these characters and gives lots of space for future expansion.
- Message Prefixes : Every message type from Grbl has a unique prefix to help GUIs immediately determine what the message is and parse it accordingly without having to know context. The prior interface had several instances of GUIs having to figure out the meaning of a message, which made everything more complicated than it needed to be.
- New OEM specific features, such as safety door parking, single configuration file build option, EEPROM restrictions and restoring controls, and storing product data information.
- New safety door parking motion as a compile-option. Grbl will retract, disable the spindle/coolant, and park near Z max. When resumed, it will perform these task in reverse order and continue the program. Highly configurable, even to add more than one parking motion. See config.h for details.
- New ‘$’ Grbl settings for max and min spindle rpm. Allows for tweaking the PWM output to more closely match true spindle rpm. When max rpm is set to zero or less than min rpm, the PWM pin D11 will act like a simple enable on/off output.
- Updated G28 and G30 behavior from NIST to LinuxCNC g-code description. In short, if a intermediate motion is specified, only the axes specified will move to the stored coordinates, not all axes as before.
- Lots of minor bug fixes and refactoring to make the code more efficient and flexible.
- NOTE: Arduino Mega2560 support has been moved to an active, official Grbl-Mega project. All new developments here and there will be synced when it makes sense to.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
List of Supported G-Codes in Grbl v1.1: - Non-Modal Commands: G4, G10L2, G10L20, G28, G30, G28.1, G30.1, G53, G92, G92.1 - Motion Modes: G0, G1, G2, G3, G38.2, G38.3, G38.4, G38.5, G80 - Feed Rate Modes: G93, G94 - Unit Modes: G20, G21 - Distance Modes: G90, G91 - Arc IJK Distance Modes: G91.1 - Plane Select Modes: G17, G18, G19 - Tool Length Offset Modes: G43.1, G49 - Cutter Compensation Modes: G40 - Coordinate System Modes: G54, G55, G56, G57, G58, G59 - Control Modes: G61 - Program Flow: M0, M1, M2, M30* - Coolant Control: M7*, M8, M9 - Spindle Control: M3, M4, M5 - Valid Non-Command Words: F, I, J, K, L, N, P, R, S, T, X, Y, Z |
Grbl is an open-source project and fueled by the free-time of our intrepid administrators and altruistic users. If you’d like to donate, all proceeds will be used to help fund supporting hardware and testing equipment. Thank you!
Wiki:
About Grbl
Grbl is a free, open source, high performance software for controlling the motion of machines that move, that make things, or that make things move, and will run on a straight Arduino. If the maker movement was an industry, Grbl would be the industry standard.
Most open source 3D printers have Grbl in their hearts. It has been adapted for use in hundreds of projects including laser cutters, automatic hand writers, hole drillers, graffiti painters and oddball drawing machines. Due to its performance, simplicity and frugal hardware requirements Grbl has grown into a little open source phenomenon.
In 2009, Simen Svale Skogsrud (http://bengler.no/grbl) graced the open-source community by writing and releasing the early versions of Grbl to everyone (inspired by the Arduino GCode Interpreter by Mike Ellery). Since 2011, Grbl is pushing ahead as a community-driven open-source project under the pragmatic leadership of Sungeun “Sonny” Jeon Ph.D. (@chamnit).
Who should use Grbl
Makers who do milling or laser cutting and need a nice, simple controller for their system that will run on the ubiquitous Arduino Uno. People who loathe to clutter their space with legacy PC-towers just for the parallel-port. Tinkerers who need a controller written in tidy, modular C as a basis for their project.
Nice features
Grbl is great for light duty production. We use it for all our milling, running it from our laptops or Raspberry Pis using superb GUIs written for Grbl to stream G-code jobs. Grbl is written in highly optimized C utilizing all the clever features of the Arduino’s Atmega328p chips to achieve precise timing and asynchronous operation. It is able to maintain more than 30kHz step rate and delivers a clean, jitter free stream of control pulses.
Grbl is for three axis machines. No rotation axes (yet) – just X, Y, and Z.
The G-code interpreter implements a subset of the LinuxCNC standard and is supported by most CAM-tools with no issues. For descriptions of these G-codes, see LinuxCNC’s superb documentation for their G-code descriptions, (G-code Quick Reference), and the Shapeoko wiki which attempts to list all codes supported by Grbl with appropriate commentary. Note that there are only a handful of deviations from the written G-code standard listed below. If you notice any other discrepancies, please let use know!
- Multiple full circle arcs with G2 and G3 arcs with a P word is not supported.
- Laser mode alters the operation of M3, M4, and spindle speed S word changes. See the Laser Mode page for details.
- Grbl-specific parking motion override control with an M56 command, where
M56 P0temporarily disables parking motions andM56/M56 Pxwithxgreater than zero re-enables them.
Supported G-Codes in v1.1
- G0, G1: Linear Motions
- G2, G3: Arc and Helical Motions
- G4: Dwell
- G10 L2, G10 L20: Set Work Coordinate Offsets
- G17, G18, G19: Plane Selection
- G20, G21: Units
- G28, G30: Go to Pre-Defined Position
- G28.1, G30.1: Set Pre-Defined Position
- G38.2: Probing
- G38.3, G38.4, G38.5: Probing
- G40: Cutter Radius Compensation Modes OFF (Only)
- G43.1, G49: Dynamic Tool Length Offsets
- G53: Move in Absolute Coordinates
- G54, G55, G56, G57, G58, G59: Work Coordinate Systems
- G61: Path Control Modes
- G80: Motion Mode Cancel
- G90, G91: Distance Modes
- G91.1: Arc IJK Distance Modes
- G92: Coordinate Offset
- G92.1: Clear Coordinate System Offsets
- G93, G94: Feedrate Modes
- M0, M2, M30: Program Pause and End
- M3, M4, M5: Spindle Control
- M7* , M8, M9: Coolant Control
- M56* : Parking Motion Override Control
(*) denotes commands not enabled in config.h by default.
Acceleration management
In the early days, Arduino-based CNC controllers did not have acceleration planning and couldn’t run at full speed without some kind of easing. Grbl’s constant acceleration-management with look ahead planner solved this issue and has been replicated everywhere in the micro controller CNC world, from Marlin to TinyG. Grbl intentionally uses a simpler constant acceleration model, which is more than adequate for home CNC use. Because of this, we were able to invest our time optimizing our planning algorithms and making sure motions are solid and reliable. When the installation of all the feature sets we think are critical are complete and no longer requires us to modify our planner to accommodate them, we intend to research and implement more-advanced motion control algorithms, which are usually reserved for machines only with very high feed rates (i.e. pick-and-place) or in production environments. Lastly, here’s a link describing the basis of our high speed cornering algorithm so motions ease into the fastest feed rates and brake before sharp corners for fast, yet jerk free operation.
Limitations by design
We have limited G-code-support by design. This keeps the Grbl source code simple, lightweight, and flexible, as we continue to develop, improve, and maintain stability with each new feature. Grbl supports all the common operations encountered in output from CAM-tools, but leave some human G-coders frustrated. No variables, no tool databases, no functions, no canned cycles, no arithmetic and no control structures. Just the basic machine operations and capabilities. Anything more complex, we think interfaces can handle those quite easily and translate them for Grbl.
New features in v1.1!
Another HUGE update! This version includes the last remaining priority features that have been long been on the to-do list. Here’s a summary of the new changes:
- Real-time Overrides : Alters the machine running state immediately with feed, rapid, spindle speed, spindle stop, and coolant toggle controls. This awesome new feature is common only on industrial machines, often used to optimize speeds and feeds while a job is running. Most hobby CNCs try to mimic this behavior, but usually have large amounts of lag. Grbl executes overrides in realtime and within tens of milliseconds.
- Jogging Mode : The new jogging commands are independent of the G-code parser, so that the parser state doesn’t get altered and cause a potential crash if not restored properly. Documentation is included on how this works and how it can be used to control your machine via a joystick or rotary dial with a low-latency, satisfying response.
- Laser Mode : The new “laser” mode will cause Grbl to move continuously through consecutive G1, G2, and G3 commands with spindle speed changes. When “laser” mode is disabled, Grbl will instead come to a stop to ensure a spindle comes up to speed properly. Spindle speed overrides also work with laser mode so you can tweak the laser power, if you need to during the job. Switch between “laser” mode and “normal” mode via a $ setting.
- Dynamic Laser Power Scaling with Speed : If your machine has low accelerations, this option will automagically scale the laser power based on how fast Grbl is traveling, so you won’t have burnt corners when your CNC has to make a turn! Enabled by the
M4spindle CCW command when laser mode is enabled. - Sleep Mode : Grbl may now be put to “sleep” via a $SLP command. This will disable everything, including the stepper drivers. Nice to have when you are leaving your machine unattended and want to power down everything automatically. Only a reset exits the sleep state.
- Significant Interface Improvements: Tweaked to increase overall performance, include lots more real-time data, and to simplify maintaining and writing GUIs. Based on direct feedback from multiple GUI developers and bench performance testing. NOTE: GUIs need to specifically update their code to be compatible with v1.1 and later.
- New Status Reports: To account for the additional override data, status reports have been tweaked to cram more data into it, while still being smaller than before. Documentation is included, outlining how it has been changed. Improved Error/Alarm Feedback : All Grbl error and alarm messages have been changed to providing a code. Each code is associated with a specific problem, so users will know exactly what is wrong without having to guess. Documentation and an easy to parse CSV is included in the repo.
- Extended-ASCII realtime commands : All overrides and future real-time commands are defined in the extended-ASCII character space. Unfortunately not easily type-able on a keyboard, but helps prevent accidental commands from a G-code file having these characters and gives lots of space for future expansion.
- Message Prefixes : Every message type from Grbl has a unique prefix to help GUIs immediately determine what the message is and parse it accordingly without having to know context. The prior interface had several instances of GUIs having to figure out the meaning of a message, which made everything more complicated than it needed to be. New OEM specific features, such as safety door parking, single configuration file build option, EEPROM restrictions and restoring controls, and storing product data information.
- New safety door parking motion as a compile-option. Grbl will retract, disable the spindle/coolant, and park near Z max. When resumed, it will perform these tasks in reverse order and continue the program. Highly configurable, even to add more than one parking motion. See config.h for details.
- New ‘$’ Grbl settings for max and min spindle rpm. Allows for tweaking the PWM output to more closely match true spindle rpm. When max rpm is set to zero or less than min rpm, the PWM pin D11 will act like a simple enable on/off output.
- Updated G28 and G30 behavior from NIST to LinuxCNC G-code description. In short, if an intermediate motion is specified, only the axes specified will move to the stored coordinates, not all axes as before.
- Lots of minor bug fixes and refactoring to make the code more efficient and flexible.
- NOTE: Arduino Mega2560 support has been moved to an active, official Grbl-Mega project. All new developments here and there will be synced when it makes sense to.
New features in v0.9!
- IMPORTANT:
- Default serial baudrate is now 115200! (Up from 9600)
- Z-Axis limit input on D11 has swapped with spindle enable D12 to support variable spindle PWM output.
- No QUEUE state: Queue was removed due to it being redundant. Holds now suspend Grbl and only allow realtime commands. Cycle start resumes, and reset exits.
- NEW Super Smooth Stepper Algorithm: Complete overhaul of the handling of the stepper driver to simplify and reduce task time per ISR tick. Much smoother operation with the new Adaptive Multi-Axis Step Smoothing (AMASS) algorithm which does what its name implies (see stepper.c source for details). Users should immediately see significant improvements in how their machines move and overall performance!
- Stability and Robustness Updates: Grbl’s overall stability has been focused on for this version. The planner and step-execution interface has been completely re-written for robustness and incorruptibility by the introduction of an intermediate step segment buffer that “checks-out” steps from the planner buffer in real-time. This means we can now fearlessly drive Grbl to its highest limits. Combined with the new stepper algorithm and planner optimizations, this translated to 5x to 10x overall performance increases in our testing! Also, stability and robustness tests have been reported to easily take 1.4 million (yes, million) line G-code programs like a champ!
- (x4)+ Faster Planner: Planning computations improved four-fold or more by optimizing end-to-end operations, which included streamlining the computations and introducing a planner pointer to locate un-improvable portions of the buffer and not waste cycles recomputing them.
- Variable Spindle Speed Output: Enables a hardware PWM output for ‘S’ G-code commands. NOTE: This feature requires a pin swap with the Z-limit D11 pin and spindle enable D12 pin to access the hardware PWM on pin D12. The Z-limit pin, now on D12, should work just as it did before.
- Compile-able via Arduino IDE!: Grbl’s source code may now be downloaded and altered, and then be compiled and flashed directly through the Arduino IDE, which should work on all platforms. See the Wiki for details on how to do it.
- G-Code Parser Overhaul: Completely re-written from the ground-up for 100%-compliance* to the G-code standard. (* Parts of the NIST standard are a bit out-dated and arbitrary, so we altered some minor things to make more sense. Differences are outlined in the source code.) We also took steps to allow us to break up the G-code parser into distinct separate tasks, which is key for some future development ideas and improvements.
- Independent Acceleration and Velocity Settings: Each axis may be defined with unique acceleration and velocity parameters and Grbl will automagically calculate the maximum acceleration and velocity through a path depending on the direction traveled.
- Soft Limits: Checks if any motion command exceeds workspace limits before executing it, and alarms out, if detected.
- Probing: The G38.2, G38.3, G38.4, & G38.5 straight probe G-code commands are now supported and connected through the A5 pin.
- Tool Length Offsets: Probing doesn’t make sense without tool length offsets (TLO), so we added it! The G43.1 dynamic TLO (described by linuxcnc.org) and G49 TLO cancel commands are now supported. G43.1 dynamic TLO works like the normal G43 TLO (NOT SUPPORTED) but requires an additional axis word with the offset value attached. We did this so Grbl does not have to track and maintain a tool offset database in its memory. Perhaps in the future, we will support a tool database, but not for this version.
- Improved Arc Performance: The larger the arc radius, the faster Grbl will trace it! We are now defining arcs in terms of arc chordal tolerance, rather than a fixed segment length. This automatically scales the arc segment length such that maximum radial error of the segment from the true arc is never more than the chordal tolerance value of a super-accurate default of 0.002 mm.
- New Grbl SIMULATOR! (by @jgeisler and @ashelly): A completely independent wrapper of the Grbl main source code that may be compiled as an executable on a computer. No Arduino required. Simply simulates the responses of Grbl as if it was on an Arduino.
- CPU Pin Mapping: In an effort for Grbl to be compatible with other AVR architectures, such as the 1280 or 2560, a new cpu_map.h pin configuration file has been created to allow Grbl to be compiled for them. This is currently user supported, so your mileage may vary. If you run across a bug, please let us know or better, send us a fix! Thanks in advance!
- Configurable Real-time Status Reporting: Users can now customize the type of real-time data Grbl reports back when they issue a ‘?’ status report. This includes data such as: machine position, work position, planner buffer usage, serial RX buffer usage.
- Updated Homing Routine: Sets workspace volume in all negative space regardless of limit switch position. Common on pro CNCs. But, the behavior may be changed by a compile-time option though. Now tied directly into the main planner and stepper modules to reduce flash space and allow maximum speeds during seeking.
- CoreXY Support: Grbl now supports CoreXY kinematics on an introductory-level. Most functions have been verified to work, but there may be bugs here or there. Please report any problems you find!
- Safety Door Support: Safety door switches are now supported. Grbl will force a feed hold, shutdown the spindle and coolant, and wait until the door switch has closed and the user has issued a resume. Upon resuming, the spindle and coolant will re-energize after a configurable delay and continue. Useful for OEMs that require this feature.
- Full Limit and Control Pin Configurability: Limits and control pins operation can now be interpreted by Grbl however you’d like, with the internal pull-up resistors enabled or disabled, or reading a high or low as a trigger. This should cover all wiring and NO or NC switch scenarios.
- Optional Limit Pin Sharing: Limit switches can be combined to share the same pins to free up precious I/O pins for other purposes. When combined, users must adjust the homing cycle mask in config.h to not home the axes on a shared pin at the same time. Don’t worry; hard limits and the homing cycle still work just like they did before.
- Additional Compile-Time Feature Options: Limit/control pin state reporting, line number tracking, real-time feed rate reporting, and more.
New features in v0.8!
A lot has happened since the v0.7. We’re pushing real hard to create a simple, yet powerful CNC controller for the venerable Arduino. Here’s a list of the new things that have come to v0.8.
- Multi-Tasking Run-time Commands: Feed hold with controlled deceleration for no loss of location, Resume after feed hold, Reset, and Status Reporting.
- Advanced Homing Cycle: Lots of configuration options for different types of machines from which axes to move when to their search directions. Limit switches may also be used as hard limits as well.
- Persistent Coordinate System Data: Work Coordinate Systems (G54-G59) and Pre-Defined Positions (G28,G30) are held in EEPROM, so they’ll always be set as you last set them.
- Check G-Code Mode: Sets up Grbl to run through your program without moving anything, so you can check whether or not you have any errors that Grbl may not like.
- Improved Feedback: Reports real-time position, what Grbl is doing, the G-code parser state, and stored coordinate offset values.
- Startup blocks: Auto-magically runs user G-code blocks at startup or reset. Can be used to set your defaults.
- Pin-outs: Cycle start, feed hold, and abort are now pinned-out to the A0, A1, and A2 pins. Just connect a normally-open switch to the pin and ground. That’s it!
- More Robust G-Code Parser with Error Checking Feedback.
- And much more!
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
v1.1f Release This release contains some minor tweaks to the streaming interface, new features, and bug fixes: [new] The $I build info output now shows two additional values separated by commas [OPT:VL,15,128]. The first value is the total number of usable planner buffer blocks, and the other value is the total number of serial RX buffer bytes available. This information is primarily for GUI handshaking. NOTE: There is always one unusable planner block (not part of the shown value) that is used for internal system purposes. [new] The $I build info includes 5 more character codes to identify various build options. See documentation for details. [new] Parking motion override control via a new M56 P0 and M56 P1command, which disables and enables the parking motion, respectively. A default override may be configured in config.h. This new feature requires both PARKING_ENABLE and ENABLE_PARKING_OVERRIDE_CONTROL enabled in config.h. Primarily for OEMs. [new] M56 now appears in the $G g-code parser state print out when parking override is enabled in g-code , when the ENABLE_PARKING_OVERRIDE_CONTROL option is enabled. [new] Spindle enable pin configuration option to alter its behavior based on how certain lasers work. By default, Grbl treats the enable pin separately and leaves it on when S is 0. The new option turns the enable pin on and off with S>0 and S=0. This only is in effect when a user enables the USE_SPINDLE_DIR_AS_ENABLE_PIN option. [fix] M4 was not allowed to work when USE_SPINDLE_DIR_AS_ENABLE_PIN is enabled. This was problematic for laser folks using the M4 command. [fix] Fixed an issue when in inverse time mode and G0’s would require a F word. [fix] Added a note in the defaults.h file that MAX_TRAVEL values must be positive. Some users were setting this negative and it was causing issues. [fix] EXTREMELY RARE bug. When AMASS is intentionally disabled and sent a motion command that is one step in length, Grbl would not actuate the step due to numerical round-off. Applied a fix to prevent the round-off issue. v1.1e Release Fixes an issue where tool number values were not tracked and reported in the g-code parser state. Added a new error code (38) to indicate an invalid tool number sent to the parser. v1.1e Release Contains a critical bug fix for alarm handling. A recent change to internal alarm codes were not handled correctly and would occasionally show the wrong code and enter an infinite loop. Re-installed optional software debouncing for hard limit switches. Documentation updates. Initial v1.1 master release! After a lengthy beta-testing cycle, v1.1 is ready for master release! All new realtime override command set to dial in a job, new officially supported laser mode with a nice dynamic laser power mode to produce consistent cuts, all new GUI interface to include a ton more real-time feedback, and a lot more! Please let us know if you run into any problems! Enjoy! |
Download GRBL OUDE VERSIES voor Arduino CNC Shield (328P) @ Github.com
Download GRBL NIEUWE VERSIES voor Arduino CNC Shield (328P) @ Github.com
Download GRBL ARDUINO MEGA voor Arduino CNC Shield @ Github.com
[#/mechanica/firmware/GRBL_(Arduino_CNC_Shield)” ]